How to Overcome the Machinist Shortage and Boost Production Capacity
Key Takeaways:
- Automation Limitations: Automation can't always address the CNC machinist shortage, especially in complex or low-volume production settings where getting a return on investment is complex
- Increasing Machine-to-Operator Ratio: Improving this ratio means that operators can manage more machines, reducing the need for hiring
- Anticipate machine stoppage: JITbase's system allows operators to know about coming on-machine interventions, enabling more efficient machine management without constant operator supervision
- Smart operator allocation: JITbase helps to make the best allocation decision by predicting accurate operator workloads
In the post-pandemic manufacturing landscape, demand has surged back to pre-2020 levels, presenting an urgent need for increased production capacity. However, manufacturers face a significant challenge: a shortage of specialized machinists, particularly in the CNC machining industry. This labor shortage is causing downtime and low productivity, as there aren't enough skilled operators to keep all machines running.
The hype of automation... and its limitations
Automation is often touted as the ultimate solution to the labor shortage, but this strategy - though essential - requires significant investments and time to implement. Moreover, automation isn't feasible in all production contexts, especially in high-mix, low-volume environments where production plans vary daily. In fact, if the production volumes are too low, the investment needed to automate the production process isn't cost-effective.
A New Solution: Increasing the Machine-to-Operator Ratio
An innovative approach to mitigating the impact of the machinist shortage is to enhance the machine-to-operator ratio. By enabling operators to manage multiple machines simultaneously, manufacturers can significantly reduce their recruiting needs.
While it's logical that automating production reduces the need for human resources, the number of machines managed by an operator in environments with little to no automation is rarely questioned.
However, it is quite easy to increase the number of machines managed by an operator when they know exactly when a machine requires manual intervention without constant supervision, meaning they don't need to stay in front of the machine.
Know when each machine requires attention
JITbase has developed a groundbreaking system that integrates scheduling capabilities with live machine data, transcending traditional machine monitoring systems that only track OEE.
The JITbase Live Guidance system informs operators not just when a machine stops, but when it will stop and what tasks are next. This proactive approach allows operators to manage more machines efficiently without having to stay in front of the machines, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
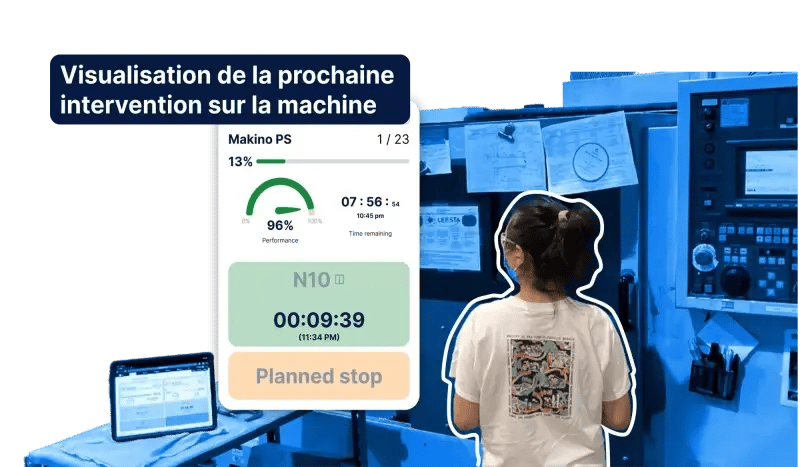
How does it work?
When a CNC program starts, JITbase retrieves the machining times and human intervention requirements. It then schedules tasks such as tool changes, M00s, inspections, part changeovers and setup operations. The scheduling system dynamically adjusts the schedule based on real-time data, much like a GPS updating its route based on current traffic conditions.
This allows operators to focus on their tasks without constantly monitoring each machine, effectively managing more machines with less stress.
Connect your machines for free and start real-time machine monitoring instantly.
Real-World Success: LEESTA Industries
LEESTA Industries, a precision machine shop in the aerospace sector, faced significant challenges with labor shortages, particularly during evening and night shifts. By implementing JITbase, LEESTA was able to maintain machine utilization with one operator managing two machines, compared to the previous one operator per machine setup.
This improvement resulted in an additional 15,600 hours of production capacity annually, translating to over $2 million worth of products.
Download the full case study here: Machine Utilization Improved by 25% using Live Guidance
Enhanced Flexibility for Operator Allocation
JITbase’s Live Guidance system not only increases productivity but also brings greater flexibility in operator allocation. Operators can manage machines that are not in their direct line of sight, allowing for more strategic placement based on production needs rather than physical proximity.
Concretely, an operator is allocated to 2 or 3 machines with CNC programs that can be managed well together, rather than being allocated to 2 or 3 machines solely because they are next to each other.
This flexibility has been a game-changer for LEESTA, enabling them to allocate operators more efficiently and maximize their use.
Conclusion: Addressing the Labor Shortage and Beyond
While automation remains an important solution for mid/long-term results, JITbase offers an immediate, cost-effective way to mitigate the impact of the machinist shortage. By improving the machine-to-operator ratio, manufacturers can boost productivity, reduce downtime, and significantly lower production costs.
As labor continues to be a critical factor in manufacturing, systems like JITbase will play a vital role in helping companies meet growing demands and stay competitive.
JITbase also uses the collected information about manual interventions to predict the workload of operators during a shift. This helps Supervisors make better decisions on the operator allocation while scheduling operations. This blog post explores in more detail how understanding operator workload can lead to a more optimized production plan.





