
What Is Manufacturing Scheduling? A Quick Overview
Key takeaways
- Manual scheduling is no longer sufficient. Advanced scheduling tools and software have become essential to streamline production planning and ensure smooth operations.
- ERP and MRP fall short when addressing the granular needs of daily planning, particularly around human tasks.
- When done right, manufacturing scheduling provides numerous benefits like on time delivery and cost savings
What Is Manufacturing Scheduling? A Quick Overview
Manufacturing scheduling is one of the critical processes that help factories and production environments operate efficiently. Whether you're running a large-scale production line or a small custom shop, scheduling can make or break your ability to meet customer demand, minimize costs, and optimize resource use. In this quick overview, we’ll dive into the basics of manufacturing scheduling, its key components, different types, and the role technology plays in streamlining the process.
What Is Manufacturing Scheduling?
Manufacturing scheduling refers to the process of planning and organizing production activities to ensure that products are made and delivered on time. It involves determining what needs to be produced, when, and in what order. The primary goal is to ensure that production flows smoothly, resources (like machines and labor) are used effectively, and deadlines are met.
At its core, manufacturing scheduling ensures that all processes — from raw material procurement to final product assembly — are coordinated in a way that minimizes delays, reduces downtime, and maximizes productivity. A well-organized manufacturing schedule is essential for achieving both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Components of Manufacturing Scheduling
- Production Orders
A production order is a request for the creation of a product or a batch of products. It serves as the starting point for scheduling and provides key information about what needs to be made, how much, and by when. These orders are typically generated based on customer demand or inventory levels. - Work Centers
Work centers refer to areas or machines where specific operations in the manufacturing process take place. Each work center might have different capacities, tools, and labor requirements. Scheduling ensures that the right tasks are assigned to the right work centers at the right times, optimizing resource usage. - Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time required to complete an entire production process, from the initial order to final delivery. It includes processing time, waiting time, and transport time. Accurate lead time calculations help in planning production schedules and ensuring that deadlines are met. - Machine and Labor Availability
Scheduling involves ensuring that the right machines and labor are available when needed. This includes factoring in maintenance schedules, workforce shifts, and machine downtime. A balanced schedule ensures maximum output without overburdening machines or employees. - Routing
Routing determines the specific sequence of operations and the path a product or component takes through the manufacturing process. It includes identifying the required machines, tools, and workstations for each step, as well as the order in which these steps occur. Effective routing ensures an efficient workflow, minimizes delays, and helps maintain quality standards.
Types of Manufacturing Scheduling
Push Scheduling
Push scheduling, often referred to as traditional scheduling, relies on forecasts or sales predictions to create a production plan. In this approach, production is "pushed" forward based on anticipated demand. While this method can be effective for products with stable demand, it may result in excess inventory and overproduction if demand is miscalculated.
Advantages:- Predictable and planned output.
- It can be effective for high-demand, repeatable products.
Challenges:
- Risk of overproduction and waste if forecasts are inaccurate.
- Difficulty in adapting to sudden demand shifts.
Pull Scheduling
Pull scheduling, often associated with the Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing approach, works by producing items only when they are needed, triggered by customer demand. This minimizes inventory levels and focuses on efficient use of resources. By only producing based on actual demand, pull scheduling helps reduce waste and increase efficiency.
Advantages:
- Reduced inventory costs.
- More flexible and responsive to market changes.
Challenges:
- Requires accurate and real-time data.
- Can be challenging in environments with high variability in demand.

The Role of Technology in Manufacturing Scheduling
In today's fast-paced manufacturing environment, manual scheduling is no longer sufficient. Advanced scheduling tools and software have become essential to streamline production planning and ensure smooth operations. Here’s how technology supports the process:
ERP Systems and Scheduling Software
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate scheduling with other business functions like inventory management, procurement, and customer orders.
- These systems can provide real-time updates and allow managers to make informed decisions about the production process. Scheduling software, on the other hand, helps automate the scheduling process, saving time and reducing human error.
MRP's Role in Manufacturing Scheduling
- MRP focuses on medium- to long-term planning, ensuring material availability by forecasting demand, managing procurement schedules, and aligning inventory with production needs.
- It prioritizes work orders and optimizes resource allocation for strategic planning.
APS's Role in Manufacturing Scheduling
- APS enhances MRP by addressing short-term scheduling needs, factoring in machine capacity, operator availability, and real-time shop floor data.
- It dynamically adjusts schedules to respond to changes, maximizing resource utilization and ensuring on-time delivery.
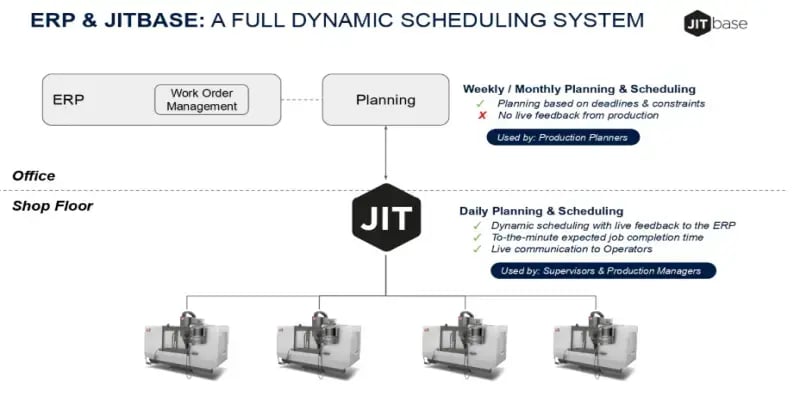
The Limitation of ERP, MRP and APS in Manufacturing Scheduling
Effective planning is the foundation of successful manufacturing operations, ensuring products are produced and shipped on time. While ERP and MRP systems excel at medium- and long-term planning by managing resources, inventory, and procurement scheduling, they fall short when addressing the granular needs of daily planning, particularly around human tasks.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) systems in manufacturing face limitations such as reliance on accurate data, difficulty adapting to real-time disruptions, and high implementation costs. They may struggle with dynamic environments requiring frequent adjustments and can face integration challenges with existing systems, reducing their overall effectiveness.
Despite the capabilities of ERP, MRP, and APS systems, many manufacturing teams still resort to using Excel for daily planning. This is primarily because these systems lack the granularity to handle the human element of production, such as manual tasks and real-time operator workload adjustments.
While ERP and MRP are powerful for medium and long-term planning, they are not designed to capture the dynamic and detailed nature of daily operations. Consequently, supervisors often turn to spreadsheets to fill these gaps, creating custom plans that account for specific machine tasks and operator assignments.
Excel, while flexible, introduces inefficiencies and potential errors. Manual data entry is time-consuming and prone to mistakes, and the lack of real-time updates means that adjustments are reactive rather than proactive. This reliance on spreadsheets highlights a significant limitation of current systems: the inability to integrate human and machine data effectively for daily scheduling.
Tools like JITbase directly address this issue by automating daily planning, capturing detailed manual task data, and providing real-time visibility into production progress. This allows supervisors to move beyond static spreadsheets, improving efficiency and accuracy while ensuring operators and machines are utilized to their fullest potential.

Benefits of Effective Manufacturing Scheduling
When done right, manufacturing scheduling provides numerous benefits that drive operational success and customer satisfaction. Key advantages include:
- On-Time Delivery
Effective scheduling ensures that products are manufactured and delivered on time, meeting customer expectations and strengthening trust. Timely delivery not only enhances a company’s reputation but also fosters long-term customer relationships. - Increased Efficiency
Proper scheduling minimizes idle time for both machines and employees. By ensuring production runs smoothly without unnecessary delays, companies achieve faster turnaround times and make the most of available resources. - Cost Savings
Efficient scheduling reduces overproduction, minimizes waste, and optimizes inventory levels. Additionally, it promotes the optimal use of resources, leading to lower energy consumption and labor costs, resulting in significant savings. - Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Delivering on promises through timely production and delivery helps businesses exceed customer expectations. A well-planned manufacturing schedule enhances reliability, improves relationships, and boosts customer loyalty.
Challenges in Manufacturing Scheduling
Although manufacturing scheduling offers many benefits, there are also challenges that manufacturers need to overcome:
Unforeseen Downtime
Unexpected disruptions, such as machine breakdowns, maintenance issues, or labor shortages, can derail even the most meticulously planned schedules. These interruptions not only delay production but can also lead to bottlenecks that ripple across the entire operation. To mitigate these risks, manufacturers must incorporate buffer times, predictive maintenance strategies, and contingency plans into their scheduling process, ensuring they can adapt swiftly to minimize downtime.
Demand Volatility
Fluctuating demand, driven by market trends, seasonality, or sudden shifts in customer preferences, can make rigid schedules impractical and unresponsive. Overproduction risks inventory excess, while underproduction leads to missed deadlines and dissatisfied customers. To navigate these complexities, manufacturers need flexible, data-driven scheduling systems capable of adapting to real-time changes in demand, ensuring resources are allocated effectively without overburdening production capacity.
This is why monitoring production and linking it to the planning is important. JITbase fills this gap by using machine data to track live production advancement and reflect it in real time in the production scheduling.
Instead of keeping the production schedule theoretical in the office, the shop floor reality is reflected in the planning which allows Production Managers and Planners to make better decisions. By using machine data for the planning, JITbase fills the gap between the back office and the shop floor.
Conclusion
Effective manufacturing scheduling is the backbone of any successful production operation, ensuring that resources are optimized, deadlines are met, and customer satisfaction is achieved. While traditional tools like ERP, MRP, and APS systems provide robust support for medium- and long-term planning, they often fall short in addressing the dynamic realities of daily operations. The reliance on manual tools like Excel highlights the limitations of these systems in capturing real-time data and accounting for human factors.
By understanding the key components, types, and challenges of manufacturing scheduling, businesses can improve their production processes, reduce waste, and keep customers happy. With the right tools and strategies, companies can achieve a streamlined and cost-effective manufacturing process that drives long-term success.
With its real-time machine data and automating capabilities, JITbase provides production managers the tools needed to make proactive decisions, improve efficiency, and adapt quickly to unexpected challenges. In a world where agility and precision are key to staying competitive, adopting advanced scheduling tools is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Embracing these technologies will not only streamline operations but also set the foundation for sustainable growth and long-term success in manufacturing.
Want to improve your manufacturing scheduling process? Explore JITbase’s tools and solutions for optimizing your production workflow and reducing waste. Contact us today to learn how we can help your business grow.






